GEO-KOMPSAT-2A User Readiness Planning
GEO-KOMPSAT-2A will load two instruments, one is AMI(Advanced Meteorological Imager) for meteorological mission and the other is KSEM(Korea Space wEather Monitor) for space weather mission.
AMI(Advanced Meteorological Imager)

KSEM(Korea Space wEather Monitor)
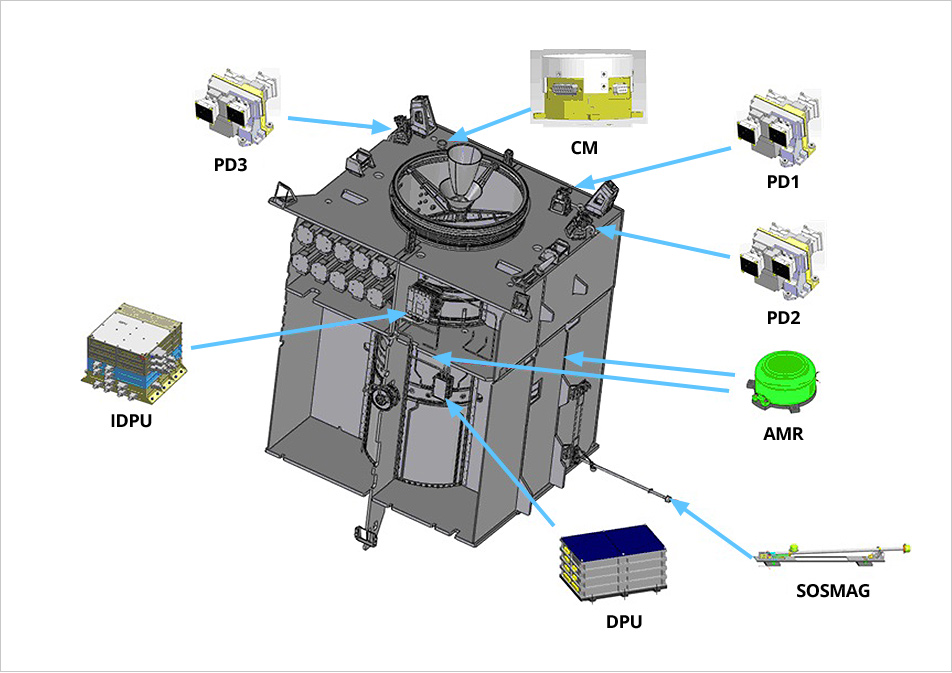
PD: Particle Detector / MG: Magnetometer / CM: Charging Monitor
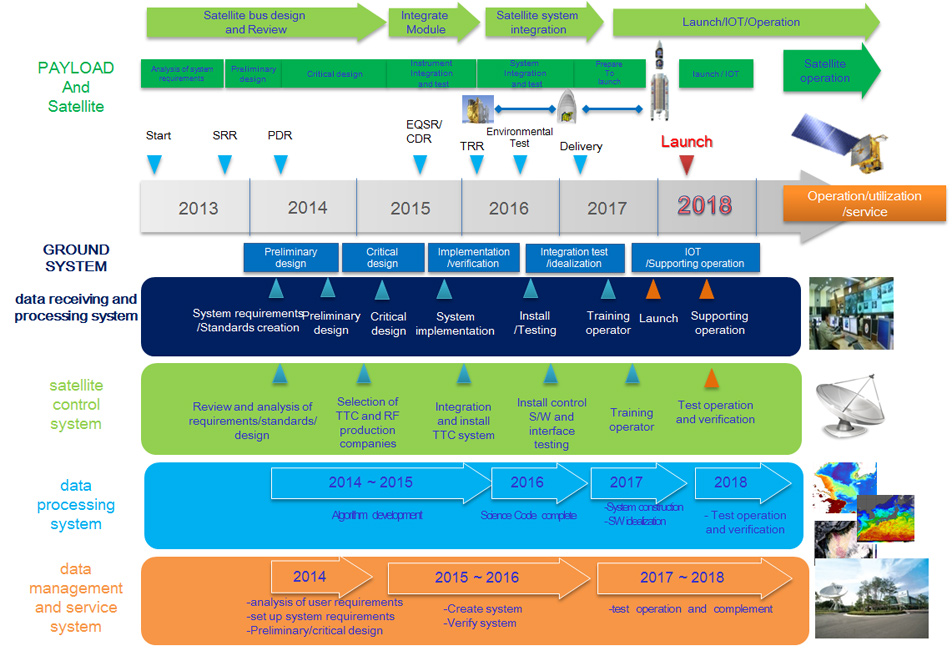
Milestone for the Geo-KOMSAT-2A
GEO-KOMPSAT-2A Instrument Performance
AMI(Advanced Meteorological Imager) with 16 channels
- 1.38 µm : favorable for cirrus cloud detection, cloud type and amount
- 2.3 µm : favorable for Land/cloud Properties
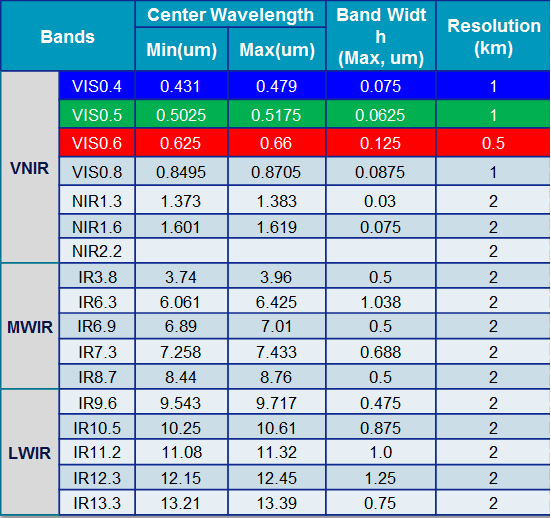
AMI(Advanced Meteorological Imager) SRF(Spectral Response Function)
| Index | AMI Band | Center Wavelength Spec Min(µm) | Center Wavelength Spec Max(µm) | AMI measured Center Wavelength(µm) | Bandwidth Spec Max(µm) | AMI measured Bandwidth(µm) | Max Out of Band Response Spec(%) | AMI Out of Band Response(%)=100% x (out of band) / (in-band) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | VIS0.4 | 0.431 | 0.479 | 0.4702 | 0.0750 | 0.0408 | 1.00% | 0.13% |
| 2 | VIS0.5 | 0.5025 | 0.5175 | 0.5086 | 0.0625 | 0.0291 | 1.00% | 0.21% |
| 3 | VIS0.6 | 0.625 | 0.66 | 0.6394 | 0.1250 | 0.0808 | 1.00% | 0.08% |
| 4 | VIS0.8 | 0.8495 | 0.8705 | 0.8630 | 0.0875 | 0.0344 | 1.00% | 0.34% |
| 5 | NIR1.3 | 1.373 | 1.383 | 1.3740 | 0.0375 | 0.0155 | 1.00% | 0.51% |
| 6 | NIR1.6 | 1.601 | 1.619 | 1.6092 | 0.0750 | 0.0410 | 1.00% | 0.31% |
| 7 | IR3.8 | 3.74 | 3.96 | 3.8316 | 0.5000 | 0.1912 | 1.00% | 0.22% |
| 8 | IR6.3 | 6.061 | 6.425 | 6.2104 | 1.0380 | 0.8397 | 1.00% | 0.39% |
| 9 | IR6.9 | 6.89 | 7.01 | 6.9413 | 0.5000 | 0.4004 | 1.00% | 0.43% |
| 10 | IR7.3 | 7.258 | 7.433 | 7.3266 | 0.6880 | 0.1823 | 1.00% | 0.53% |
| 11 | IR8.7 | 8.44 | 8.76 | 8.5881 | 0.5000 | 0.3552 | 1.00% | 0.19% |
| 12 | IR9.6 | 9.543 | 9.717 | 9.6210 | 0.4750 | 0.3789 | 1.00% | 0.28% |
| 13 | IR10.5 | 10.25 | 10.61 | 10.3539 | 0.8750 | 0.4683 | 1.00% | 0.38% |
| 14 | IR11.2 | 11.08 | 11.32 | 11.2285 | 1.0000 | 0.6636 | 1.00% | 0.31% |
| 15 | IR12.3 | 12.15 | 12.45 | 12.3651 | 1.2500 | 1.1072 | 1.00% | 0.20% |
| 16 | IR13.3 | 13.21 | 13.39 | 13.2870 | 0.7500 | 0.5566 | 1.00% | 0.16% |
KSEM(Korea Space wEather Monitor)
| Sensor | Specification |
|---|---|
| Energetic Particle Detector |
|
| Magnetometer (ESA, SOSMAG) |
|
| Satellite Charging |
|
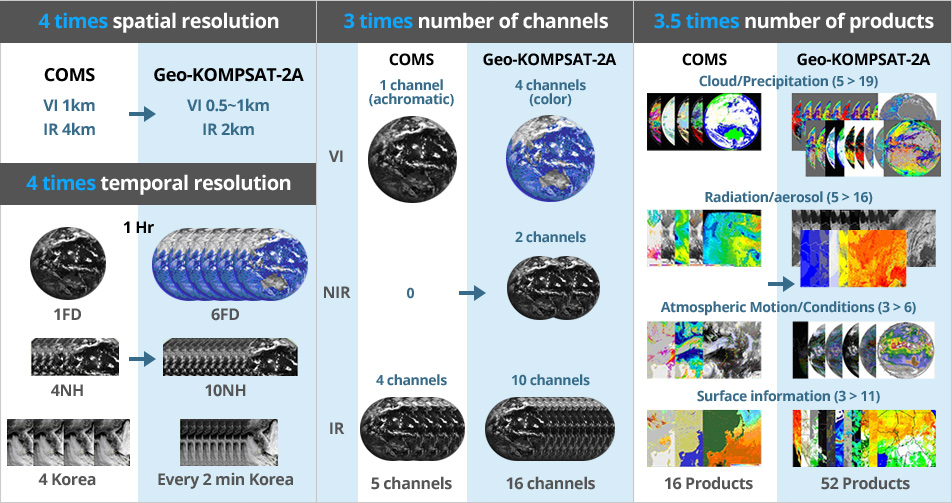
COMS MI vs. Geo-KOMSAT-2A
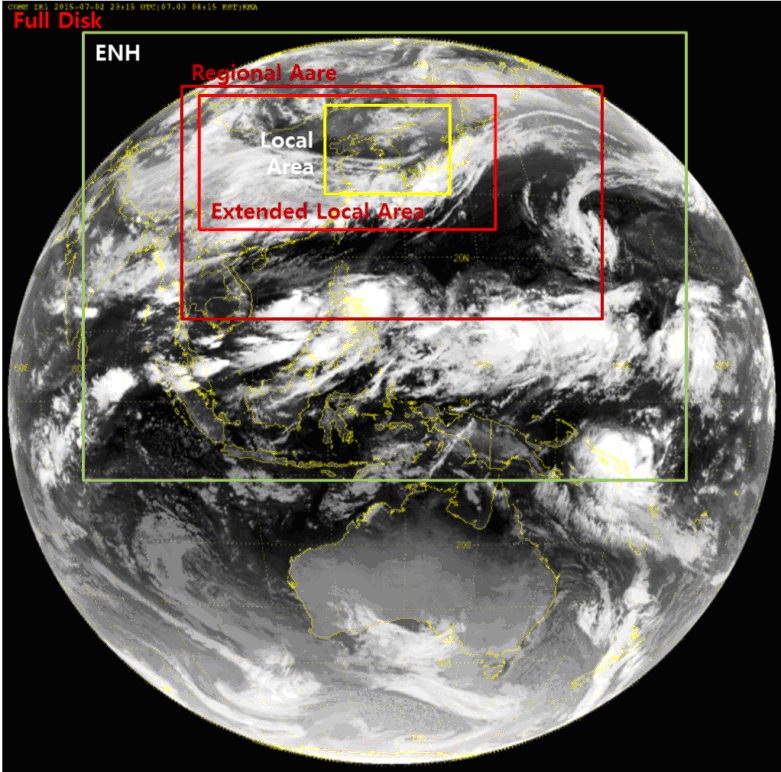
GEO-KOMPSAT-2A Areas of Coverage and Observation Schedule
Observation Scan Patterns
- Full Disk (FD)
- Regional Area (RA) : 6200 X 5900 km (EW X NS)
- Extended Local Area (ELA) : 4300 X 2900 km (EW X NS)
- Local Area (LA) : 1000×1000 km (EW X NS)
| Observation | Scene | Duration(sec.) | EW | NS | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global | FD | 356 | 17.8º | Diameter centered at nadir | |
| Regional | RA | 148 | 6200km | 5900km | RA scene center at 15.956ºN, 127.218ºE |
| ELA | 66 | 3800km | 2900km | ELA scene center at 37.588ºN, 124.044ºE | |
| LA | 38 | 1000km | 1000km | Outer dege within ±11º NS and EW of nadir | |
| Operational | 1FD+4ELA | 600 | Custom timeline collecting four ELA scenes at ~2.5 minute intervals plus one Full Disk scene | ||
Observation Area and Schedule
- Plan 1: Full Disk (1) + ELA (4) / 10 minutes
- Plan 2: Full Disk (1) + RA (2) / 10 minutes
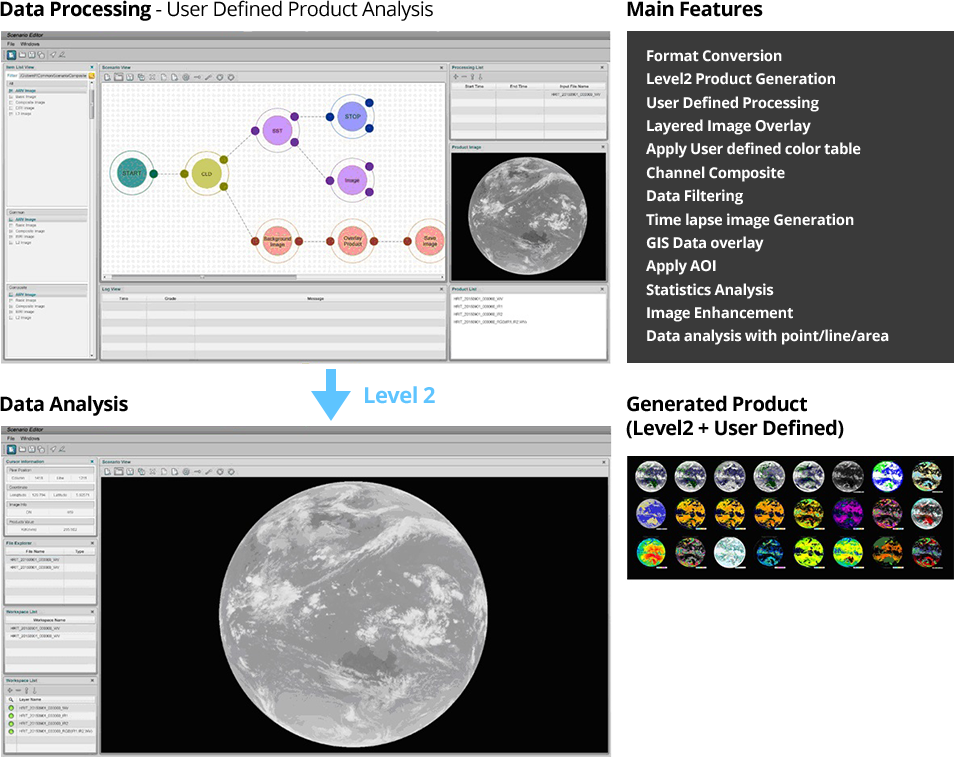
GEO-KOMPSAT-2A Software Tools and Test Data
Image Processing Tools are under development
- Image processing/analysis tool for Linux and PCs
- Scenario-based (User-defined) Level 2 meteorological products generation tool
- The function of real time/non-real time image format conversion (library) will be developed
GEO-KOMPSAT-2A Training and Resource
All documents including ATBD (Algorithm Theoretical Basis Documents) of Level-2 products from GK-2A satellite are now being prepared and will be available after 2018. To meet the user’s needs and operational performance, user community composed of scientists, researchers and operational forecasters communicate with each other through monthly science meeting, seminars, or annual workshops. NMSC/KMA is also developing user-oriented GK-2A image processing tools for internal and international users.
On the other hand, Centre of Excellence (CoE) of KMA will provide an international training course on “Improvement of Meteorological Satellite Data Analysis and Application Capacity” from 2016 to 2018 through the support of KOICA (Korea International Cooperation Agency). The objective of this course is to improve analysis and application competence in the various fields such as forecasting, marine, climate, environment, hydrology etc. using GK-2A and other LEO satellite data.
The first training is scheduled for 24 days from 10 October to 2 November, 2016 and 26 participants from 17 countries such as Nepal, Bangladesh, Solomon Islands, Timor-Leste, Cambodia, Laos, Sri Lanka, Vietnam, Myanmar, Papua New Guinea, Fiji, Mongolia, Philippines, Indonesia, Uzbekistan and Bhutan, will attend the course. The training will focus on the quantitative and qualitative use of COMS and GK-2A data and products, satellite image interpretation and analysis for weather forecasting, fundamental RGB techniques, various application methods for climate, environment and hydrology fields to enhance understanding on the next generation satellite of GK-2A.
At the occasion of Asia-Oceanic Meteorological Satellite Users’ Conference in Songdo, Korea from 21 to 27, November 2016, 2days’ training event (21~22, Oct.) is also planned, which is related to data processing and application on nowcating of next generation satellites such as Himawari-8, GOES-R, FY-4, and GK-2A.
The detailed module of KMA’s international training is as below table.
| Module | Lectures & Discussions |
|---|---|
|
Module 1. Korean meteorological satellite program |
|
|
Module 2. COMS data processing and products |
|
|
Module 3. satellite imagery interpretation |
|
|
Module 4. Applications of GEO and LEO satellite data |
|
|
Module 5. KMA’s GEO-KOMPSAT-2A satellite |
|
|
Module 6. Next generation satellite data processing tools |
|